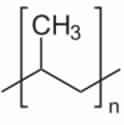
Homopolymer is a high corrosion resistant polypropylene material which exhibits excellent tensile strength and stiffness at elevated temperatures. These polypropylene possess excellent resistance to organic solvents and degreasing agents as well as electrolytic attack..
Compared to low or high density polyethylene, homopolymer has a lower impact strength, but superior working temperature and tensile strength. In addition, polypropylene is light weight, stain resistant and has a low moisture absorption rate.